Characteristics of Op-Amp
The characteristics of Op-Amp is very important because we can compare the performance of various Op-Amp ICs and select the best suitable Op-Amp for any desired application.
 |
| Equivalent Circuit of an Op-Amp |
The characteristics of an Op-Amp
are divided into two types namely AC characteristics and DC characteristics.
The AC characteristics include the frequency response, frequency compensation,
Bandwidth, slew rate, and stability of Op-Amp whereas the DC characteristics
include input offset voltage, the input offset current, input bias current, and
thermal drift, etc.
Let’s understand each characteristic one by one.
Open Loop Voltage Gain
Open-loop voltage gain is defined as the differential gain of an Op-Amp in the open-loop mode of operation. Note that open-loop mode is the mode of operation without any feedback. The open-loop gain is very high. It is denoted by AV.
Input Offset Voltage
The input offset voltage is defined as a small differential voltage that is applied at the input of the Op-Amp to make the output voltage zero. It is denoted by Vios.
Ideally, the output voltage of an Op-Amp should be zero for a zero-input voltage. But practically, due to unbalancing in the differential input stage of the Op-Amp, the output is not zero. So, we have to apply a small differential voltage at the input stage of the Op-Amp to make the output voltage zero.
The value of input offset voltage is temperature-dependent and it is about a few mV ranges.
Output Offset Voltage
The output voltage produced due to input offset voltage is called output offset voltage. It is denoted by Voos.
Input Offset Current
Input Offset Current is defined as the algebraic difference between current flowing into the inverting and non-inverting terminals of the Op-Amp. It is denoted by Iios.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as
Input Bias Current
Input Bias Current is defined as the average value of the current flowing into the inverting and non-inverting terminals of the Op-Amp. As shown in the figure, the current flowing into non-inverting input is IB2 and the current flowing into inverting input is IB1.
Hence, the input bias current is given by
The value of input bias current is temperature-dependent and it should be as low as possible.
Differential Input Resistance
Differential Input Resistance is defined as the equivalent resistance which can be measured at either the inverting or non-inverting input terminal of the Op-Amp with the other terminal connected to the ground. It is also called the input resistance of the Op-Amp. It is denoted by Ri.
The value of differential input resistance should be as high as possible. It is about a few MΩ for the Op-Amps if a transistor is used as an input and about to GΩ for the Op-Amps if FET is used as an input.
Output Resistance
Output Resistance is defined as the resistance which can be measured at the output terminal of the Op-Amp with input short-circuited.
The value of the output resistance should be as small as possible because it improves the output voltage regulation and current sourcing capacity.
CMRR
CMRR stands for Common Mode Rejection Ratio is defined as the ratio of differential gain to common-mode gain. It is denoted by ƿ.
PSRR
PSSR stands for Power Supply Rejection Ratio is defined as the change in input offset voltage of an Op-Amp due to the change in the supply voltage of an Op-Amp. It is also known as the Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio (SVRR) or Power Supply Sensitivity (PSS).
Mathematically PSRR can be expressed as,
Ideally, the value of PSRR should be zero and practically it should be as small as possible.
Slew Rate
The Slew Rate of an Op-Amp is defined as the maximum rate of change of output voltage per unit time. It is expressed in Volts/microseconds.
Mathematically PSRR can be expressed as,
Bandwidth
The bandwidth of the Op-Amp is the range of frequencies over which all the signal frequencies are amplified equally.
The bandwidth of an Op-Amp should be capable of amplifying the signals from 0 Hz frequency. It should be as large as possible.
Gain Bandwidth Product
Gain Bandwidth Product is defined as the bandwidth of Op-Amp when the voltage gain is unity (1). It is also called unity-gain bandwidth or small signal bandwidth.

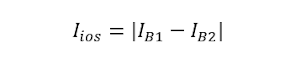




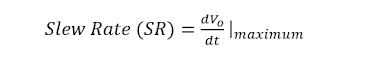



No comments:
Post a Comment